Mapping Wi-Fi Network Range with GRASS, Kismet, and python
Aug 12, 2007 metroadminUpdate to a previous post on mapping wireless network information with GRASS, kismet, and a custom python script. This time, some modifications to the python XML-processing script so that we can work directly with the Kistmet-xxx.gps files. Processing the .gps files allows one to produce a shapefile from each trip to the field. The shapefiles can be combined in a GIS (like GRASS) with simple vector processing (i.e. patching). Example steps are presented below, complete with an RST-based interpolation of wifi card signal and noise observations.
Approximately 7500 observations (signal, noise, location, network id, location) were collected with kismet/gpsd and processed with a custom python script (see attached file at bottom of page). Wireless signal maps for a specific network were created in GRASS via interpolation.
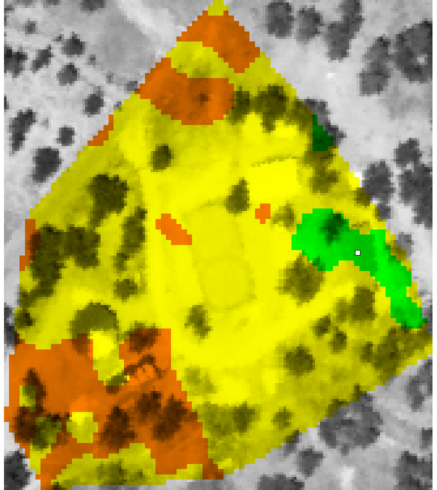
wifi signal quality map: good quality (green), fair (yellow), poor (orange)
Vector Processing
# convert Kismet .gps file into shapefiles ./process_kismet_gpslog.py -f Kismet-Aug-09-2007-4.gps -o wifi1.shp ./process_kismet_gpslog.py -f Kismet-Aug-10-2007-1.gps -o wifi2.shp # # import into GRASS v.in.ogr dsn=wifi1.shp out=wifi1 --o v.in.ogr dsn=wifi2.shp out=wifi2 --o # # patch them into a single file: not forgetting the attribute table v.patch -e in=wifi1,wifi2 out=wifi # # make a convex hull to use as an interpolation mask v.hull in=wifi out=wifi_hull
Raster Processing
# setup interpolation res g.region res=2 vect=wifi # convert wifi convex hull into raster mask v.to.rast in=wifi_hull out=interp_mask use=val val=1 # interpolate via RST # signal level, but only for a single network v.surf.rst in=wifi zcol=signal elev=food_sig maskmap=interp_mask where="ssid = '00:13:10:88:AB:E2'" --o # set new colormap r.colors map=food_sig color=rainbow # # noise level, for all networks v.surf.rst in=wifi zcol=noise elev=noise maskmap=interp_mask --o # # generate contours for later r.contour in=food_sig out=food_sig_cont levels=-190,-200,-210 --o
Overview map with NAIP imagery contours suggest areas of optimal network coverage
g.region res=1 d.rgb r=naip.red g=naip.green b=naip.blue d.vect food_sig_cont width=2 col=black d.vect net_center icon=basic/box fcol=red size=10 d.vect wifi col=blue icon=basic/cross1 size=5 where="ssid = '00:13:10:88:AB:E2'" d.out.file res=2 out=wifi_overview format=png --o
Signal and Noise maps interpolated via RST
# make the signal map g.region res=1 d.erase d.his i=naip.gr h=food_sig d.vect net_center icon=basic/box fcol=white d.barscale bcolor=none tcol=white d.legend map=food_sig at=5,8,35,95 col=white d.out.file out=wifi_signal format=png --o # # make the noise map: d.erase d.his i=naip.gr h=noise d.vect net_center icon=basic/box fcol=white d.barscale bcolor=none tcol=white d.legend map=noise at=5,8,35,95 col=white d.out.file out=wifi_noise format=png --o