Home » Software » GRASS GIS: raster, vector, and imagery analysis » Raster Operations » Simple Comparision of Two Least-Cost Path Approaches
Simple Comparision of Two Least-Cost Path Approaches
Feb 19, 2008 metroadmin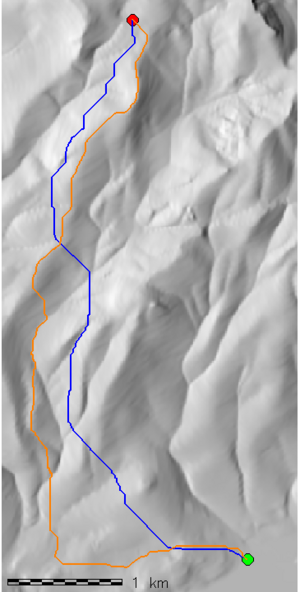 Premise:
Premise:
Simple comparison between the least-cost path as computed by r.walk vs. r.cost. Default parameters, unity travel friction, and λ = 1 were used with r.walk. Slope percent was used as the accumulated cost for r.cost. Test region similar to that used in a previous navigation example.
Results:
- r.walk
- Shorter total path (6.03 km)
- Tendency to stay mid-slope, and cross large drainage at the gentlest possible position
- r.cost
- Longer total path (7.12 km)
- Tendency to follow drainages upstream-- not always possible in steep terrain
Code:
Prep work see attached files at bottom of page to re-create
# generate cost "friction" maps # unity friction for r.walk r.mapcalc "friction = 1.0" # use slope percent as the friction for r.cost r.slope.aspect elev=elev slope=slope format=percent
Compute the least-cost path via two methods
# compute cumulative cost surfaces r.walk -k elev=elev friction=friction out=walk.cost start_points=start stop_points=end lambda=1 # Peak cost value: 14030.894105 r.cost -k in=slope out=cost start_points=start stop_points=end # Peak cost value: 11557.934493 # compute shortest path from start to end points r.drain in=walk.cost out=walk.drain vector_points=end r.drain in=cost out=cost.drain vector_points=end
Vectorize least-cost paths for further analysis
r.to.vect -s in=walk.drain out=path_1 r.to.vect -s in=cost.drain out=path_2 # add DB column for length calculation v.db.addcol path_1 columns="len double" v.db.addcol path_2 columns="len double" # how long are the two paths? v.to.db path_1 option=length column=len units=me # 6.03 km v.to.db path_2 option=length column=len units=me # 7.12 km
Simple map
d.rast shade d.vect start icon=basic/circle fcol=green size=15 d.vect end icon=basic/circle fcol=red size=15 d.vect path_1 width=2 col=blue d.vect path_2 width=2 col=orange
Sample the elevation raster at a regular interval
# add a vertex every 100m along each line # this will create two tables for each # path_1_pts_1 <-- original atts # path_1_pts_2 <-- original cat + distance along the original line v.to.points in=path_1 out=path_1_pts -i dmax=100 v.to.points in=path_2 out=path_2_pts -i dmax=100 # add column for elevation values v.db.addcol map=path_1_pts layer=2 columns="elev double" v.db.addcol map=path_2_pts layer=2 columns="elev double" # upload elev values for profile graph v.what.rast vector=path_1_pts raster=elev layer=2 column=elev v.what.rast vector=path_2_pts raster=elev layer=2 column=elev # dump profiles to CSV files db.select path_1_pts_2 fs="," > p1.csv db.select path_2_pts_2 fs="," > p2.csv
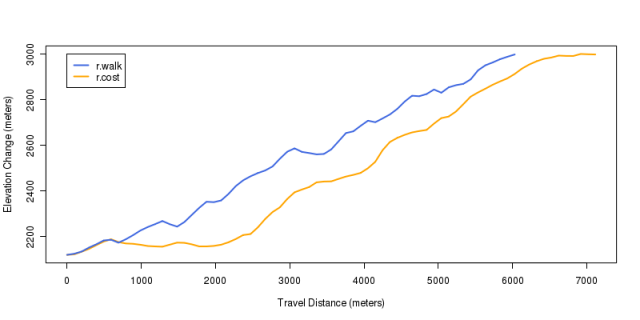
Least Cost Path Comparision Profile
Plot an elevation profile for each path
## startup R
R
## load data from previous steps
p1 <- read.csv('p1.csv')
p2 <- read.csv('p2.csv')
## can't guarantee that the two lines will be in the same direction (a r.to.vect thing?)
## p1 is correct, p2 is reversed
## make a nicer plot
## library(Cairo)
## Cairo(type='png', bg='white', width=800, height=400)
plot(elev ~ rev(along), data=p2, type='l', col='orange', lwd=2, xlab='Travel Distance (meters)', ylab='Elevation Change (meters)')
lines(elev ~ along, data=p1, col='RoyalBlue', lwd=2)
legend(0, 3000, legend=c('r.walk', 'r.cost'), col=c('RoyalBlue', 'orange'), lwd=2)
Attachments:
Links:
Mapping Wifi Networks with Kismet, GDAL, and GRASS
Raster Operations
Using R and r.mapcalc (GRASS) to Estimate Mean Topographic Curvature
Software
- General Purpose Programming with Scripting Languages
- LaTeX Tips and Tricks
- PostGIS: Spatially enabled Relational Database Sytem
- PROJ: forward and reverse geographic projections
- GDAL and OGR: geodata conversion and re-projection tools
- R: advanced statistical package
- GRASS GIS: raster, vector, and imagery analysis
- Generic Mapping Tools: high quality map production